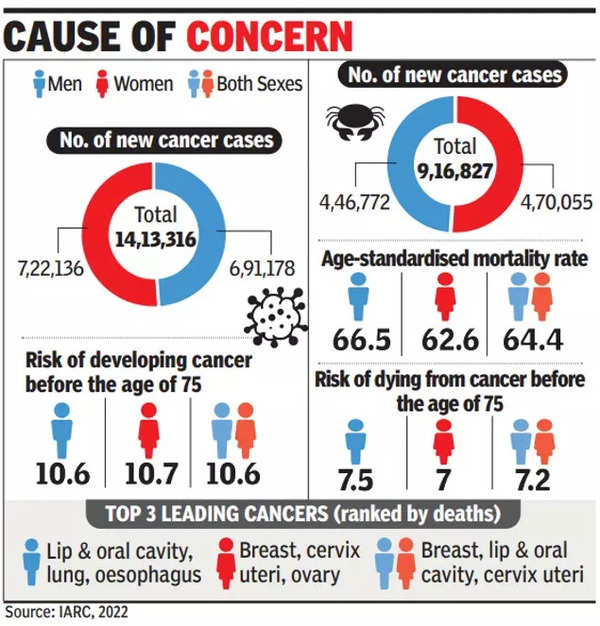
According to data on the prevalence of cancer globally released by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) ahead of World Cancer Day on Sunday, the risk of dying from cancer before the age of 75 years in India is 7.2%. The corresponding figure for both the US and Canada is 8.8%.
According to Dr Cary Adams, head of Union for International Cancer Control (UICC), despite the progress made in early detection of cancers and the treatment and care of cancer patients, significant disparities in treatment outcomes exist not only between high- and low-income regions of the world, but also within countries.
“Where someone lives should not determine whether they live. Tools exist to enable governments to prioritise cancer care, and to ensure that everyone has access to affordable, quality services. This is not just a resource issue but a matter of political will,” Dr Adams was quoted as saying in a statement issued by IARC, the specialised cancer agency of WHO.
The IARC has predicted over 35 million new cancer cases in 2050, an increase of 77% from the estimated 20 million cases in 2022.
IARC said that globally, the rapidly growing cancer burden reflected both population ageing and growth, along with changes in people’s exposure to risk factors, several of which are associated with socio-economic development.
Tobacco, alcohol, and obesity were key factors behind the increasing incidence of cancer, with air pollution still a key driver of environmental risk factors, it said.
According to a study published in eClinicalMedicine – an open access journal published by The Lancet – nearly 2.25 lakh people died in India in 2020 due to cancer caused by preventable risk factors, namely alcohol consumption, tobacco smoking, excess weight, and Human Papilloma Virus (HPV). Maximum 1.1 lakh deaths were caused by cancers related to tobacco smoking, followed by HPV (89,100), alcohol consumption (41,600) and excess body weight (8,000).
HPV is a group of more than 200 related viruses. Some of these viruses can cause cancer, for example cancer of the cervix. Vaccines are available to reduce the risk of HPV infection.
In the eClinicalMedicine study, researchers collected population attributable fractions of the four risk factors from global studies and applied these to estimates of cancer deaths in 2020 to obtain preventable cancer deaths in India and six other countries, namely China, Russia, Brazil, South Africa, the UK, and the US.
They found that the maximum number of cancer deaths attributable to the four preventable risk factors took place in China (11.4 lakh), followed by India (2.2 lakh), US (2.2 lakh), Russia (1.2 lakh), Brazil (73,500), UK (59,500) and South Africa (18,100).
Tobacco smoking was by far the biggest driver of preventable cancer deaths, causing 1.3 million deaths – more than two thirds of the preventable cancer deaths due to these four risk factors.