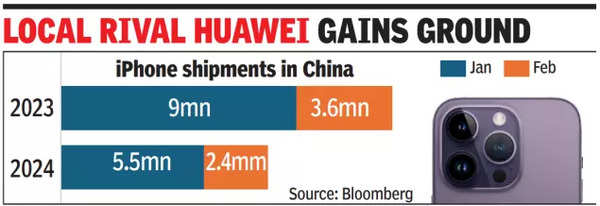
But evidence is mounting that, for many in China, the iPhone no longer holds the appeal it used to. During the first six weeks of the year, historically a peak season for Chinese shoppers to spring for a new phone, iPhone sales fell 24% from a year earlier, according to Counterpoint Research, which analyses the smartphone market.
Meanwhile, sales for one of Apple’s longstanding Chinese rivals, Huawei, surged 64%. It’s a challenging time for Apple. This month, Apple has taken two regulatory hits: a European Union fine of nearly $2 billion for anticompetitive music streaming practices and a US government lawsuit claiming Apple violated antitrust laws.
For a decade, China has been the iPhone’s most important market after the US and accounted for roughly 20% of Apple’s sales. Now the company’s grip on China could be dislodged by a series of factors: a slowdown in consumer spending, growing pressure from Beijing for people to shun devices made by US companies and the resurgence of national champion Huawei.
“The golden time for Apple in China is over,” said Linda Sui, a senior director at TechInsights, a market research firm. One of the biggest reasons is the rising tension between the US and China over trade and technology, Sui said. Without a significant lessening of geopolitical stress, it will be difficult for Apple to retain its position.
Few American companies have more to lose from these heightened tensions than Apple, whose newest handset, the iPhone 15, went on sale in Sept. “Five years ago, Apple had really strong branding in China – people would bring tents to wait through the whole night outside the Apple Store for the next product launch,” said Lucas Zhong, a Shanghai-based analyst at Canalys, a market research firm. “The iPhone 15 launch wasn’t nearly as popular.”
Apple declined to comment. Apple started selling iPhones in China in 2009. The last time it was losing ground to Huawei, in 2019, the Trump administration inadvertently extended Apple a lifeline by restricting US technology firms from dealing with Huawei. But the restrictions also forced Huawei to develop its own wireless chip and operating system.